The crankcase ventilation system is a vital component of modern internal combustion engines. It serves to manage blow-by gases, which are produced during the combustion process and can lead to various engine issues if not properly ventilated. When the crankcase ventilation system becomes disconnected or malfunctions, it can trigger diagnostic trouble codes such as P04DB, indicating that the system is not functioning as intended. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and solutions related to a disconnected crankcase ventilation system, providing comprehensive insights for vehicle owners and enthusiasts.
The crankcase ventilation system's primary function is to control the flow of gases produced in the engine's crankcase. These gases can include unburned hydrocarbons and other harmful emissions that, if left unchecked, may lead to increased pressure within the engine, oil leaks, and reduced fuel efficiency. A malfunctioning or disconnected crankcase ventilation system can result in a range of problems, from minor performance issues to significant engine damage.
To better understand this topic, we will explore the following aspects:
- What is the Crankcase Ventilation System?
- Common Causes of Disconnection
- Symptoms of a Malfunctioning System
- Diagnosis and Solutions
- Preventative Measures
What is the Crankcase Ventilation System?
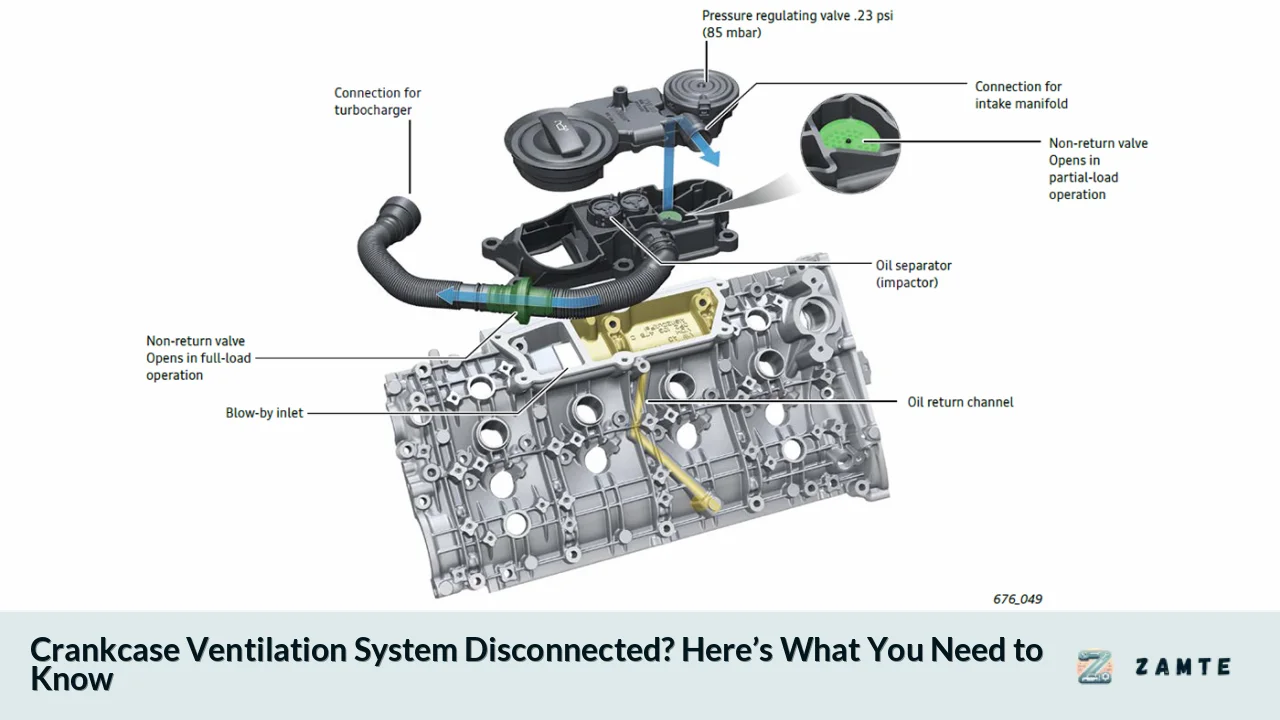
The crankcase ventilation system (CVS) is designed to remove blow-by gases from the engine's crankcase. These gases are formed when combustion gases escape past the piston rings into the crankcase. The CVS typically consists of several components:
- PCV Valve: The Positive Crankcase Ventilation valve regulates airflow between the crankcase and intake manifold.
- Breather Hose: This hose connects the valve cover to the intake manifold, allowing gases to be drawn into the engine for combustion.
- Oil Separator: This component helps separate oil from the blow-by gases before they re-enter the intake.
The proper functioning of this system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and minimizing harmful emissions.
Common Causes of Disconnection
Several factors can lead to a disconnected or malfunctioning crankcase ventilation system:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, hoses and valves can become brittle or cracked due to exposure to heat and oil, leading to disconnections.
- Improper Installation: Aftermarket modifications or repairs may inadvertently disconnect or improperly install components of the CVS.
- Clogged Components: Accumulation of sludge or debris can clog hoses or valves, preventing proper airflow.
- Faulty Sensors: In some cases, sensors that monitor airflow may fail, triggering error codes related to the CVS.
Key Points on Causes
- Regular maintenance can help identify wear before it leads to disconnection.
- Aftermarket modifications should be performed carefully to avoid disrupting existing systems.
Symptoms of a Malfunctioning System
When the crankcase ventilation system is disconnected or malfunctioning, several symptoms may arise:
- Check Engine Light: One of the most common indicators is a check engine light accompanied by error codes such as P04DB.
- Rough Idle: A malfunctioning PCV valve can cause irregular airflow, leading to unstable engine idle.
- Increased Oil Consumption: If blow-by gases are not properly managed, they can lead to excessive oil consumption.
- Oil Leaks: High pressure in the crankcase may force oil past seals and gaskets, resulting in leaks.
- Poor Engine Performance: A disconnected CVS can lead to decreased power output and poor acceleration due to imbalanced air-fuel mixtures.
Summary of Symptoms
1. Check Engine Light
2. Rough Idle
3. Increased Oil Consumption
4. Oil Leaks
5. Poor Engine Performance
Diagnosis and Solutions
Diagnosing issues with a disconnected crankcase ventilation system involves several steps:
1. Visual Inspection: Start by inspecting all hoses and connections for signs of wear or disconnection.
2. Check for Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for diagnostic trouble codes related to the CVS.
3. Smoke Test: A smoke test can help identify leaks in hoses or connections by introducing smoke into the system and observing where it escapes.
4. Component Testing: Test individual components such as the PCV valve for proper operation; it should open and close correctly based on engine vacuum levels.
Solutions
- Replace Damaged Hoses/Valves: If any components are found to be damaged or worn out, they should be replaced immediately.
- Reattach Disconnected Parts: Ensure all hoses are securely connected; if any were loose or disconnected during maintenance or repairs, reattach them properly.
- Clean Clogged Components: If any parts are clogged with sludge or debris, clean them thoroughly before reinstallation.
Preventative Measures
To avoid future issues with your crankcase ventilation system:
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule routine inspections of your vehicle’s engine components, including hoses and valves associated with the CVS.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing components, opt for high-quality OEM parts rather than cheaper aftermarket alternatives that may not fit properly.
- Monitor Engine Performance: Pay attention to changes in engine performance or unusual symptoms that may indicate CVS issues early on.
Conclusion
A disconnected crankcase ventilation system can lead to significant engine problems if not addressed promptly. Understanding its function, recognizing symptoms of malfunction, diagnosing issues effectively, and implementing preventative measures are crucial steps for vehicle owners. By staying vigilant about your vehicle's maintenance needs and addressing any concerns regarding the crankcase ventilation system promptly, you can ensure optimal performance while minimizing harmful emissions.
FAQs
- What does P04DB code mean?
The P04DB code indicates that there is a problem with the crankcase ventilation system being disconnected. - How do I know if my PCV valve is bad?
Common signs include rough idle, increased oil consumption, and a check engine light. - Can I drive with a disconnected crankcase ventilation system?
It's not recommended as it may lead to increased emissions and potential engine damage. - How often should I check my crankcase ventilation system?
Regular inspections should be part of your vehicle's routine maintenance schedule. - What should I do if I suspect a problem with my CVS?
Consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair as soon as possible.